Personality Tested Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator personality test is one of the most well-known personality instruments, but it has not been fully accepted by the scientific community.
This is because it is not a test that meets the standards of reliability and validity. Nevertheless, the test is still very popular.
For example, who has not read about the INFJ personality: the profile that is characterized by introversion, intuition, feeling and judgment?
Or maybe the INFP personality appeals to you, or the “healer” as Carl Jung himself called it. One thing is for sure: the letter combinations clearly attract people’s attention and arouse curiosity.
It would not be wrong to say that it is still one of the most widely used instruments despite its limitations. It is a type of inventory in the form of a self-report.
In other words, you can do it yourself online and discover what personality type you have.
It follows the standard developed by Katherine Briggs and her daughter Isabel Briggs-Myers in 1942. They in turn based the standard on Carl Jung’s book Psychological Types.
You may not know it, but Jung was the one who introduced concepts such as introversion and extroversion. He also established eight personality types from this dichotomy.
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator personality test uses this typology and further develops it one step further. Continue reading to learn more about this test.
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator personality test – purpose, characteristics and reliability
Isabel Myers and her mother Katherine were fascinated by Jung’s theory and undertook to use the theory in a practical way to help people better understand individual differences.
In other words, they wanted to deepen their knowledge of human personality and thus get closer to human potential and our limitations.
They began to develop this indicator during World War II. They had already published articles of great interest, such as “Meet Yourself: How to Find Yourself Through the Personality Box” and “Up from Barbarism” (translated titles).
When they presented the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator personality test for the first time, they did so in order to facilitate the choice of job. The goal was to help people choose jobs that increased their happiness and fulfillment.
Two years later, they improved this instrument by publishing a manual on how to use it. In 1956, the name was finally changed to its current form.
What information do we get from the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator personality test?
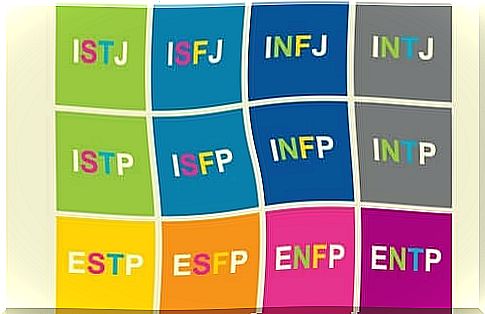
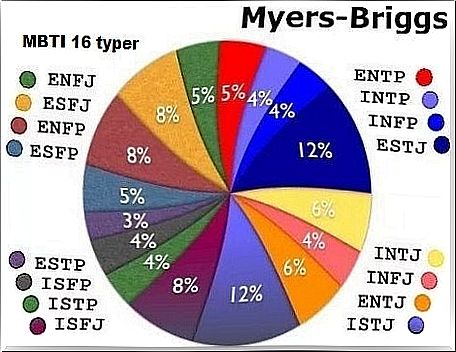
The test tells you how to get information about your personality type. This test describes up to 16 very specific types.
The goal of it is to facilitate your self-discovery; to know how to process the world, how to behave and how to relate to it. You can also discover your strengths to perhaps change direction in working life.
You can also get a better understanding of how compatible you are with other people.
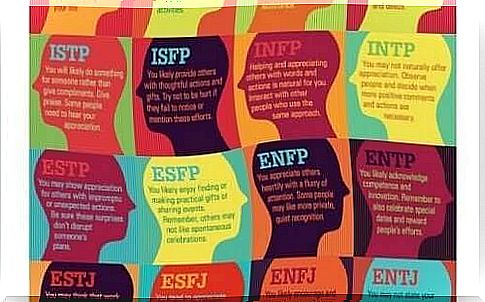
What does the test measure?
This personality test is based on four scales:
Extroversion (E) – Introversion (I)
Note that everyone has both extroversion and introversion. However, there is a tendency towards one of them.
Perception (S) – Intuition (N)
This dimension refers to two ways of interacting with what surrounds you. Perceiving people tend to pay attention to reality through their senses.
Intuitive, in turn, allows itself to be swept away by abstract factors such as emotions, patterns and impressions. These people have better imagination and are more thoughtful.
Thinking (T) – Feeling (F)
This dimension offers information on how to make decisions. Some are more logical and objective (logical thinking) while others are more emotional.
Judging (J) – Perceptive (P)
The last scale says how you interpret your surroundings and how you make decisions. There are those who judge and always make firm decisions, while others are more flexible, perceptive, sensitive and adaptable.
The results you get in these four dimensions will be expressed in the form of a series of letters that define your personality type:
- ISTP – The Craftsman
- ISFJ – The Protector
- ISFP – The Artist
- INFJ – Lawyers
- INFP – Healer
- INTJ – Architects
- INTP – The Thinker
- ESTP – The convincing
- ESTJ – The director
- ESDP – The Brave
- ESFJ – The custodian
- ENFP – The Master
- ENFJ – The sensor
- ENTP – The converter
- ENTJ – The master

Use and reliability of the Myers-Briggs test
As we mentioned at the beginning of the article, the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator personality test is not an instrument that has been generally accepted by experts. It is an equally popular and controversial instrument.
To begin with, its descriptions are somewhat vague in their description of behavior. So much so that the scientific community has pointed out that this instrument fails in what is called the Forer effect.
So it’s just a description to feel immediately identified.
But despite its criticism, low reliability and alleged lack of validity, it is often used in working life. A research study by Allen Hammer explains that it is used in schools to help students choose a profession.
It is also a recurring test in the field of personal development as well as a test people take online to find out a little more about themselves.
However, it will be considerably more useful if a specialist expert explains the results and gives you adequate guidance with regard to them. No one can deny that it is an interesting and attractive resource.